Chronic kidney disease or (CKD) meaning indicates a state where the kidneys of a particular individual are not working well permanently. Kidneys also assist in purifying your blood. They filter out waste and unwanted substances in the blood.
CKD results in a severe condition and thus additional research should be conducted to provide more comprehensive knowledge on the outcomes of this disease. It can lead to kidney failure untreated and kidney failure is fatal. Kidneys are vital body organs because they play a major role in filtering the waste products in the blood. If they are not employed then poisonous matters accumulate in the bloodstream.
Even more symptoms are; weakness, swelling of the feet, and change in the pattern of urination. It may grab you by the throat or turn your stomach or something like that. Therefore, the management of this ailment entails taking foods, medications, and, at times, a kidney transplant.
What is Chronic Kidney Disease?
The chronic kidney disease (also represented by the abbreviation CKD) is actually a kidney disease that is characterized by the gradual progressive loss of the kidney’s ability to function for a longer time span. Kidneys are organs which are involved in the cleaning of blood through the removal of waste products and fluid and the capacity to perform these tasks decreases as one progresses with the disease through the various stages of CKD.
CKD is characterized sometimes by the absence of symptoms in initial stages hence could be discovered only through a check-up. Recently CKD has been classified into five stages beginning from the early stage impairment in stage 1 to the final stage stage 5, wherein kidney failure requiring dialysis or kidney transplantation is inevitable.
Causes of Chronic Kidney Disease
CKD can be caused by a number of factors which include chronic glomerulonephritis, diabetic nephropathy, hypertensive nephrosclerosis, polycystic kidney disease, nephrosclerosis, and Kidney interstitial diseases among other conditions. Common causes include:
Diseases: if not diagnosed properly and not properly managed the high concentration of blood sugar can affect the kidneys negatively.
Hypertension: It tightens on the blood vessels and this also leads to the damaging of kidneys, in case of high blood pressure.
Glomerulonephritis: This is known as nephritis – inflammation that can occur in the kidney’s filtering mechanism or in small blood vessels present in the kidney.
Polycystic Kidney Disease: A disease passed on in families whereby the formation of cysts occurs in the renal organ.
Kidney infections and kidney stones: Kidney infections signify disease and reduced kidney performance; since Katy has had recurrent infections and stones, this will exacerbate her situation.
Prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract: Other diseases such as benign prostatic hyperplasia which is an enlargement of the prostate gland can also put a limit on the actual flow of urine.
Read More: Urinery Tract Infection
Symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease
In early cases of CKD, there are often no signs of the condition because the rest of the kidneys work in parallel to the damaged parts to complete the tasks.
Fatigue: Fatigue is a phenomenon that is manifested by at least one or even both of the following signs Fatigue is a state where one feels exhausted and drained.
Swelling: Primarily in the ankle, the feet, and in the hands mainly due to edema.
Changes in urination: In other words, Orange or brownish urine, or if you have less or more frequent urine than you usually do.
Shortness of breath: This is because there exists what is known as pulmonary edema; that is, there is an excess fluid in the lungs.
Nausea and vomiting: Growing out of the accumulation of toxicant waste products.
Muscle cramps: When the attacks do happen though, they are mostly at night time.
Itchy skin: This is due to consolidation of metabolites in the blood levels.
This is as a-result of buildup of metabolites in the bloodstream. Classically it presents with poor appetite, weight loss and this is one of the conditions we see typical marasmic patients.
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease
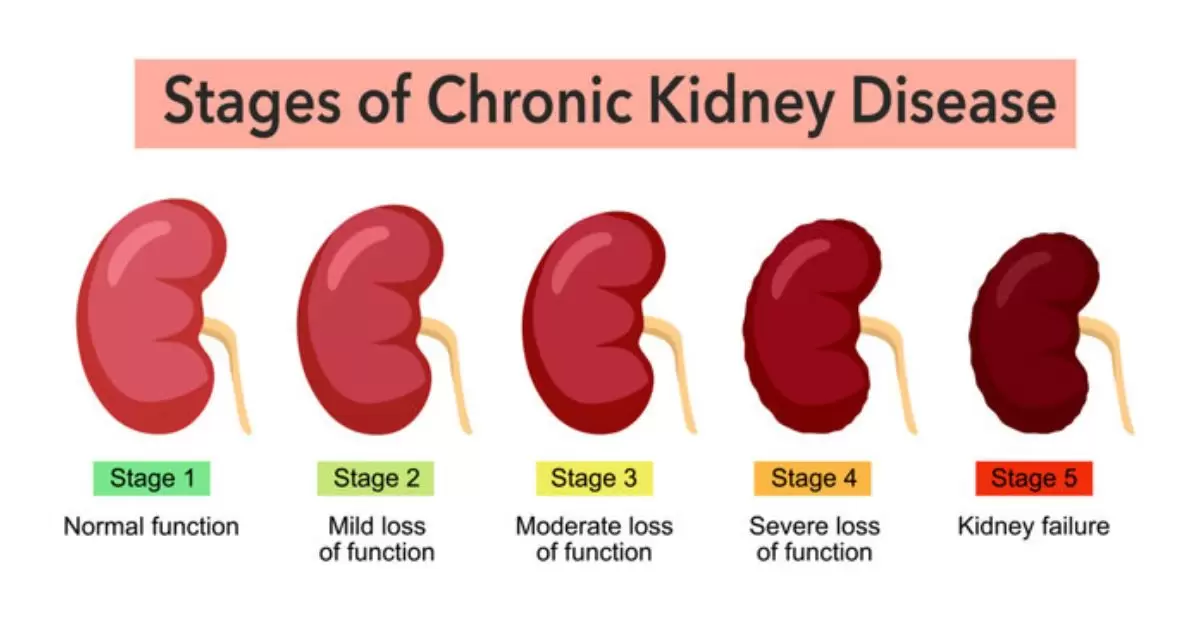
These are the main stages of chronic kidney disease:
Chronic kidney disease is divided into five stages, which are based on the estimated GFR (eGFR), which reflects the efficiency of the kidneys in removing wastes from the bloodstream.
Stage 1 of CKD is defined where a patient has a normal or even elevated GFR of 90 or above, yet indices of nephron dysfunction exist.
Stage 2 is considered as a moderate reduction in GFR with rating ranging from 60 to 89.
Stage 3 demonstrates a mildly lower GFR of 30-59; the majority subdivides it into stage 3A with a GFR of 45 to 59 and stage 3B with a GFR between 30 and 44.
Stage 4 characterizes a very low GFR in the range of 15-29.
Stage 5 presents the kidney failure, accompanied by a GFR of less than 15, which can only be treated through dialysis or the acquisition of a new kidney.
A gradual worsening of these symptoms is observable as CKD progresses through stages, from mild fatigue and presence of edema during early stages via anemia, mineral bone disease as well as fluid overload during further stages. The progression can be slowed, and crucial interventions to improve the quality of life of patients diagnosed with CKD can be instituted if the disease is diagnosed early and appropriately managed through diet modification and medications.
How to Diagnose Kidney Disorder
Kidney disorder refers to a process of investigation that leads to the determination of the extent of the kidney disorder through analysis and investigation. One of the most frequent means of assessing renal failure is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) test which measures the kidney’s clearing capacity. Other routine tests that are done include creatinine blood test, and urine test to determine protein and blood levels for CKD.
Diagnostic procedures like USG or CT scan can be employed to assess the shape and size of the kidneys as well as unusual features present. It is however important to detect CKD early, as it commonly presents without symptoms until the kidneys have been damaged to a significant extent. Annual check-ups for high-risk patients that include people with diabetes, hypertension or a history of kidney illnesses are important.
Read More: Colon Cancer
Can kidney disorder result in Failure of the kidneys?
Yes, kidney disorders can also result in kidney failure if not well controlled. Which means that the kidneys are gradually becoming non-functional or rather they are in the process of being damaged. This can degenerate and become worse over time and in the extreme, the kidneys can even fail to function. Kidneys, when they fail, cannot be able to remove waste products from the blood which is pretty hazardous to the body.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) progresses to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), also known as kidney failure. When kidneys get to this stage, it means that they have failed to function as they used to in handling the body’s requirements. It is a condition that requires life support measures such as dialysis or a kidney transplant. Timely diagnosis and appropriate management of CKD is important in order to reduce the risk of its advancement into kidney failure.
Innovative Treatments and Research
Thus, investigation of CKD treatment continues and potential treatments for it are changing with each passing day. Some promising areas include:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cell therapy promises transformative treatment of patients with damaged kidneys and this area is being actively researched.
- Gene Therapy: The proposed treatment of CKD through gene therapy seeks to restore the function of damaged genes. While it is still currently undergoing exploration for possible treatment, it presents great potential for a future application.
- New Medications: New drugs are being brought to our disposal due to research in different fields of pharmacy that seek to address various factors associated with end-stage CKD. For instance, SGLT2 inhibitors intended for diabetes type 2 treatment have shifted to managing CKD as well.
Advanced Therapies for Severe CKD
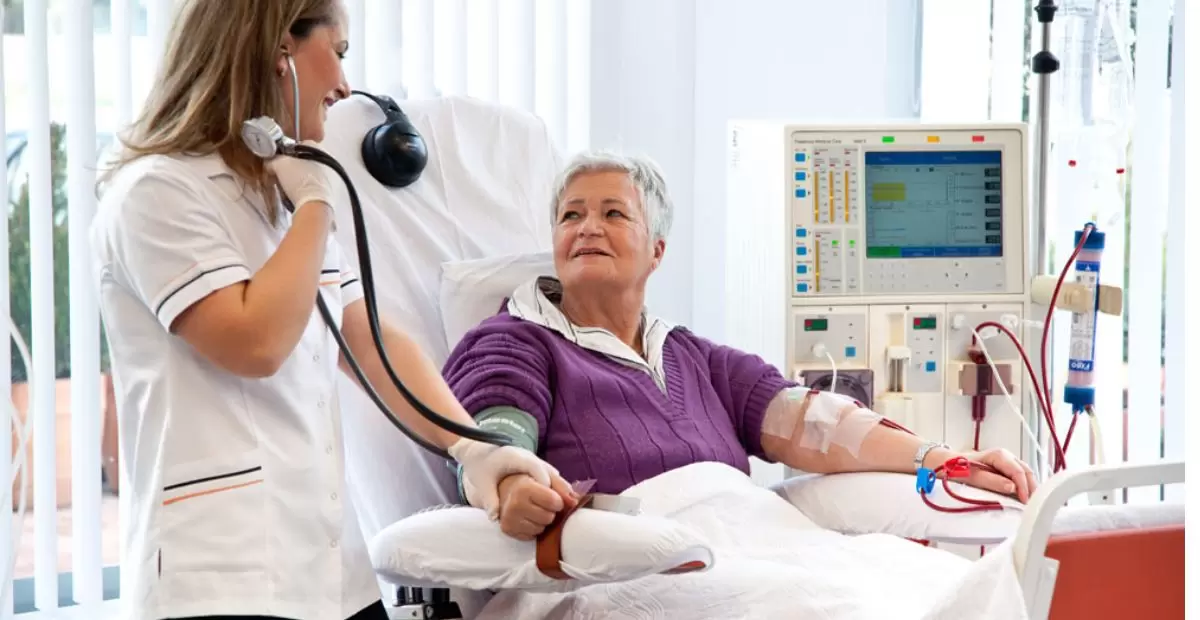
Additional investigations for CKD may be needed especially when the stage is 4 or 5 for the patient. These include:
Dialysis
Kidney failure patients need dialysis treatment, it is a process which is extremely important to them and prolongs their lives. It functions like the kidney through the elimination of wastes and any excess liquid in the bloodstream. There are two main types of dialysis. There are two main types of dialysis:
Hemodialysis: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy means that a gallbladder is removed through small incisions. This process often takes three sessions in a week at any dialysis facility or center.
Peritoneal Dialysis: The abdominal wall shown in the figure is a fold of tissue that is utilized to filter blood within the body. This is done at home and is flexible compared to the other two types of lessons, as mentioned in the previous section
Kidney Transplantation
In terms of therapeutic options, kidney transplant is regarded as the most efficient for the patients with ESRD. It is a surgical procedure that entails transplanting of a healthy kidney into the patient, this kidney can be gotten from a living or a deceased person. Transplantation is the best option to live a normal life but always have immunosuppressive drugs since rejection is ever.
Router: Transplantation is thought to be the best way of living a normal life but the problem is, the person is always on immunosuppressive drugs since there is always the risk of rejection.
Managing Chronic Kidney Disease
Dialysis, medications, changes in daily life, and regular follow-ups from a physician are some of the ways through which CKD can be managed. Some of the factors that should be put into consideration in managing CKD include the following. The patients suffering from diabetes or hypertension need to monitor their blood pressure and levels of glucose in their blood, should minimize the consumption of salt and control their weights through certain foods and movement.
Medications: ACE inhibitors or ARBs may be used to help protect the kidneys, and addressing dietary needs such as a low protein intake in addition to low potassium and phosphorus help lessen the kidneys’ workload. Moreover, it is important to visit a health care provider from time to time in order to assess the progress of kidney disease and make some alterations to the plan of treatment if needed.
Medical Management: Significant components of self-management include medical management as well as embracing emotional and social support in coping with CKD. To manage the psychological aspect of the disease, then patients should ask their families, friends, and other affected patients in support groups to help them.
Lifestyle changes: Other measures include changing one’s diet, non-use of tobacco products, a low or no alcohol intake, and exercise among others, and these measures can be very effective in slowing down the disease and improving the quality of life of the patients. Since there are disease-related components of CKD, it is advisable for the patients to consult healthcare professionals on how they can enhance their well-being.
Dietary Recommendations for CKD Patients
In the care of CKD, diet plays an important role to be emphasized. Managing one’s diet is important in preventing the worsening of symptoms and maintaining the progression of the disease. Here are some key dietary guidelines for CKD patients. Here are some key dietary guidelines for CKD patients:
Control Protein Intake
That is why the proposed product is very useful in health, however excessive amounts of protein may harm the kidneys. Peptidemia of mild to moderate severity in CKD, patients on dialysis are recommended to take moderate protein intake. There is advice on proven sources of proteins such as lean meats, fish, eggs and even dairy products.
Manage Sodium Intake
Sodium intake is important in controlling the fluid build up and high blood pressure within CKD patients. Here are some ways on how one can go about reducing the intake of salt; One has to avoid foods such as processed foods, canned foods and salty snacks. Avoid using certain ingredients such as salty, sweet, sour and bitter foods and instead opt for herbs and spices that add flavor to foods.
Limit Phosphorus and Potassium
High levels of phosphorus and potassium can be harmful to CKD patients. High levels of phosphorus and potassium can be harmful to CKD patients:
Phosphorus: Consequently, it can be found in dairy products, nuts, seeds, and can be produced endogenously by the human body. Hemodialysis patients in particular should use lower phosphorus products and could possibly require phosphate-binding agents.
Potassium: These are some examples that can be found in bananas, oranges, potatoes, tomatoes among others. It is important that patients regulate their consumption and prefer foods with low potassium levels, such as fruits and vegetables.
Fluid Management
Sensible measures should be taken for a patient’s intake of fluids, and often patients have low urine output. It can be observed that excessive fluid accumulation is associated with features like swelling and difficulty breathing while inadequate amounts cause conditions like dehydration. Patients should avoid taking ‘’high’ volume fluid of their own choice but take fluid as recommended by their healthcare provider.
Healthy Fats
Include them from the monounsaturated fat foods like olive oil, healthy fats abounding in avocados and omega-3 fat foods like fatty fish. These include fats that are good for the body and useful in reducing inflammation in the body.
Avoiding High Sugar Foods
For CKD patients with diabetes, one must first maintain blood glucose at a certain level. Reducing the intake of s particular type of meal such as candies, sweets, and soft drinks also assists in controlling blood sugar.
Specific Foods Beneficial for CKD Patients
Here are some kidney-friendly foods that can be incorporated into a CKD diet. Here are some kidney-friendly foods that can be incorporated into a CKD diet:
Red bell peppers: It is poor in potassium and rich in vitamins A and C.
Cabbage: It is Low in calories; These vegetables contain high dietary fiber, vitamins, and phytochemicals.
Cauliflower: High in the vitamin C content and are good substitutes for high potassium foods.
Garlic: Enhances the taste and does not require supplementation of salt, has health benefits associated with it.
Onions: High in vitamins and minerals; rich in antioxidants, low in potassium.
Apples: Potassium content is low while fiber and anti-inflammatory properties are high.
Berries: Among fruits, potassium poor and antioxidant rich blueberries, strawberries and raspberries can be mentioned.
Egg whites: A high quality protein source which is also low in K/D ratio.
Fish: Containing a significantly high amount of Omega 3 fatty acids which has an anti-inflammatory function.
Read More: Mediterranean Diet
Living with Chronic Kidney Disease
Owing to the chronic and progressive nature of the disease, its management and monitoring is constant. To adopt the necessary modifications to treatment plans and changes in lifestyle, the patients have to integrate themselves with the healthcare team. Here are some tips for managing daily life with CKD.Here are some tips for managing daily life with CKD:
Regular Medical Appointments: What patients can do is visit the nephrology clinic more often, so that the doctor specialized in treating kidneys will be able to closely monitor the function of the kidneys and modify the treatment accordingly. Haemoglobin, blood chemistry, kidney function, liver function, coagulation profile, and urine analysis measure the advancement of disease and any complications.
Emotional Support: Actually, the life affected by CKD can be emotionally burdensome. It is crucial that patients receive assistance from family members or support groups on the matter. Counseling or therapy may also be beneficial for the children and young people of the family.
Staying Informed: The knowledge on CKD empowers the patient. Knowledge about the illness, the available courses of action and approaches to control this disease empowers the patient to make rational choices on issues affecting him or her.
Planning for Dialysis or Transplant: In the latter stages of CKD the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant may be required. Anticipating these possibilities therefore involves the process of becoming knowledgeable about the processes involved in donor selection and through boardroom discussions with relevant healthcare personnel.
Preventing Chronic Kidney Disease
It is always easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. While not all cases of CKD can be prevented, certain lifestyle choices can reduce the risk. While not all cases of CKD can be prevented, certain lifestyle choices can reduce the risk:
Maintain a Healthy Diet: Kidneys can benefit from a diet that is free from junk foods, fried foods, and foods high in salt, cholesterol, and saturated fats while including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy products.
Stay Hydrated: It also assists the kidneys to carry out its functions of filtering waste better in the body once you take the right amount of water.
Exercise Regularly: Exercise fitness is good for managing high blood pressure and diabetes.
Monitor Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar: Screening helps in the early diagnosis of high blood pressure and diabetes and treatment can therefore be administered on time.
Avoid Overuse of Medications: Examples of such agents include; non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs which, when taken in large amounts, are toxic to the kidneys.
Limit Alcohol and Avoid Smoking: That can damage the kidney and worsen the condition of CKD as well as ESRD.
Conclusion
Chronic kidney disease is a severe, selective, persistent, and chronic ailment that impacts an impressive number of patients globally. It is therefore essential to assess the cause, signs, and phases of the illness since early diagnosis and treatment are key factors in addressing this condition. In the study of CKD, prescribed medications, a kidney-friendly diet, exercise, and other general lifestyle changes can assist in the delay of illness progression.
The most severe type of CKD, of course, can be treated with advanced interventions like dialysis and kidney transplants, which will give the patient a better quality of life. The aims of managing CKD are physical check-ups, support, and patient education focusing on renal illness. Through these key actions, patients with CKD should effectively intervene and consult doctors on how to live full lives despite the disease.